Copper(II) arsenate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(II) arsenate
| |
| Other names
Copper arsenate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
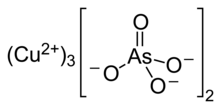
| Cu3(AsO4)2 | |
| Molar mass | 468.48 g/mol |
| Appearance | blue or bluish green powder |
| Density | 5.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) |
| insoluble | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
7.95×10−36[1] |
| Solubility | soluble in ammonia, dilute acids |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is or .
Uses
[edit]Copper arsenate is an insecticide used in agriculture. It is also used as a herbicide, fungicide, and a rodenticide. It is also used as a poison in slug baits.
Copper arsenate can also be a misnomer for copper arsenite, especially when meant as a pigment.
Natural occurrences
[edit]Anhydrous copper arsenate, Cu3(AsO4)2, is found in nature as the mineral lammerite.[3] Copper arsenate tetrahydrate, Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, occurs naturally as the mineral rollandite.[4]
Related compounds
[edit]Copper arsenate hydroxide or basic copper arsenate (Cu(OH)AsO4) is a basic variant with CAS number . It is found naturally as the mineral olivenite. It is used as an insecticide, fungicide, and miticide. Its use is banned in Thailand since 2001.[5]
See also
[edit]- Calcium arsenate
- Chromated copper arsenate
- Lead arsenate
- Paris Green (copper acetoarsenite)
- Scheele's Green (copper arsenite)
References
[edit]- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–188. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0150". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Hawthorne, F. C. (1986). "Lammerite, Cu3(AsO4)2, a modulated close-packed structure" (PDF). American Mineralogist. 71: 206–209.
- ^ Sarp, H.; Černý, R. (2000). "Rollandite, Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, a new mineral". Eur. J. Mineral. 12: 1045–1050. doi:10.1127/0935-1221/2000/0012-1045.
- ^ "Banned pesticides (Sorted by common name)". Archived from the original on 2005-11-22. Retrieved 2006-01-14.
